Technology
New ‘Hobbit’ fossils discovered on the Indonesian island of Flores
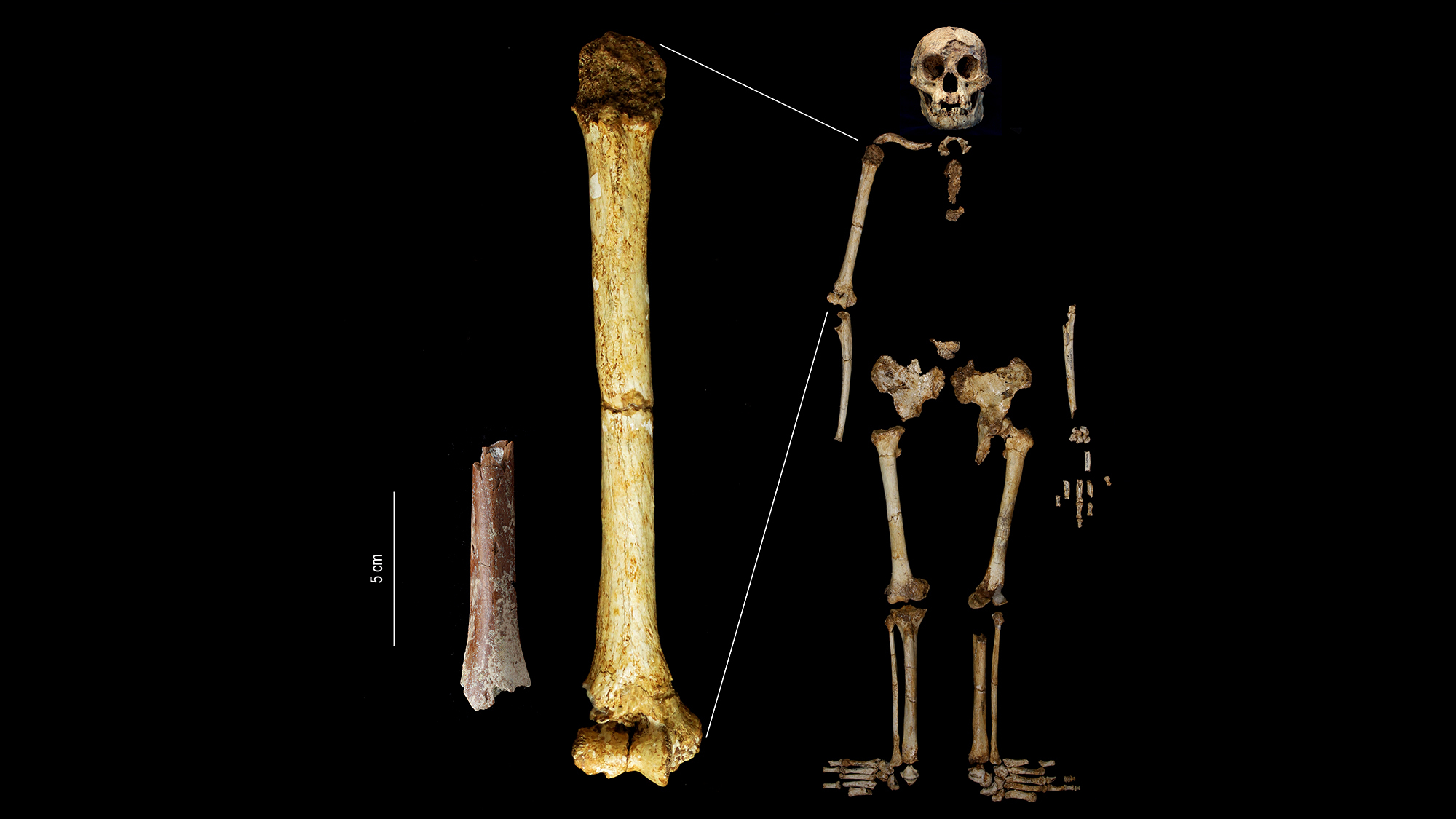
An international team of archaeologists and other researchers has found new fossils belonging to extremely rare early human species on the Indonesian island of Flores. Homo floresiensis was compared by scientists with the Hobbits of JRR Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings series due to their small size. The three approximately 700,000 year old bones shed light on the evolution of Homo floresiensisor the ‘Hobbits’ of Flores.
These newly discovered fossils are described in detail in A study published Aug. 6 in the journal Nature communication And include the first bones from under the head of one of these humanoids.
[Related: Lucy, our ancient human ancestor, was super buff.]
Animals of unusual size
A small human species makes scientific sense in Indonesia because it is known for non-human animals of unusual size. Small in body relatives of elephants called Stegodons, huge 15 pounds of rats, huge crocodilesAnd more were once roaming through this crowd of biodiversity.
Evidence from these early humans was first discovered in 2003In the Liang Bua cave by a team that is also led by the the late archaeologist Mike Morwood. Archaeological evidence suggests that humans were only about four feet tall, had small brains, and lived only 50,000 years ago. Currently, Homo sapiens had long been established in southern Australia.
However, there is still much debate about how these hominins in Southeast Asia became so small, and about their origins. Some have assumed so Homo floresiensis was a smaller descendant of the early Asiatic homo erectus. Another theory is that they are a late surviving remnant of an older hominin species from Africa that predates homo erectus. If this is the case, it could also be a descendant of Homo habilis or the infamous and super strong “Lucy” (Australopithecus afarensis).
When did they get so small?
The fossils in here new study were found further away from Liang Bua Cave, in Mata Menge. This open-air site is located approximately 74 kilometers east of the cave in the sparsely populated tropical grasslands of the So’a Basin. Earlier, archaeologists have found several hominin fossils There, including a jaw clip and six teeth from a layer of sandstone that was deposited by a stream about 700,000 years ago.
[Related: Neanderthals may have been early risers.]
Also the new fossils dates around 650,000 years before the Liang Bua-Hergensigenigen. They belong to at least three individuals who may even have slightly smaller jaws and teeth than the original Homo floresiensis copies, which implies the Flores people developed their small body size early.
However, previous excavations at Meta Menge were still missing an important piece of the puzzle. The postcranial elements–Botten from under the head – of this species still had to be uncovered. Without this it could not be confirmed that these people were at least as small as, if not smaller than Homo floresiensis.
Some critical bones
It is important that the team that worked on this research, the first postcranial element associated with it Homo floresiensis. They discovered a distal shaft of an adult humerus, or the lower half of the upper arm bone.
Digital microscopy of fossils indicates that the small upper arm belonged to an adult. The team was able to use bone length to calculate body height, and believed this was so about 3.2 feet long. This is about five centimeters shorter than the estimated height of the 60,000-year-old Homo floresiensis skeleton found in Liang Bua Cave (about 4 feet high).

“This 700,000-year-old adult humerus is not only shorter than that of Homo floresiensis“It is the smallest upper arm bone known from the hominin fossil record worldwide,” said Adam Brumm, co-author and archaeologist at Griffith University in Australia, said in a statement. “This very rare specimen confirms our hypothesis that the ancestors of Homo floresiensis were extremely small in body size; However, the small proportions of this limb bone now reveal that the early ancestors of the ‘Hobbit’ were even smaller than we had previously thought.”
Mata Menge’s two teeth are also small in size. One also has similar shape features that are most consistent with early homo erectus from the island of Java. However, this similarity does not support the hypothesis that Homo floresiensis evolved from an earlier and primitive type of hominids.
This requires more digging into the fossil record putting the bigger story together of this small group of human relatives.
“The evolutionary history of the Flores hominins is still largely unknown,” says Brumm. “However, the new fossils strongly suggest that the ‘Hobbit’ story did indeed begin when a group of early Asian hominids known as homo erectus somehow became isolated on this remote Indonesian island perhaps a million years ago, and underwent a dramatic reduction in body size over time.”













