Business
Protect your business against phishing attacks
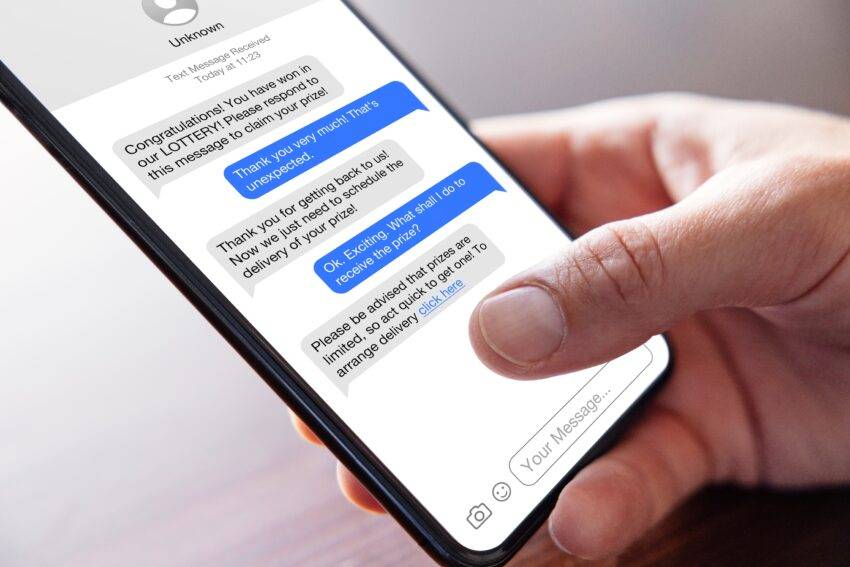
Cybersecurity is a “cat and mouse game” in which attackers are aware of many of the security measures organizations use and quickly develop strategies to circumvent them.
As part of this, knowing how to identify a phishing email is a crucial step toward protecting your organization from cyber threats.
A phishing attack is a form of cybercrime where attackers target individuals via email, phone, or text messages and impersonate a reputable or well-known individual to trick individuals into sharing sensitive information. This is a growing problem for businesses of all sizes, across all industries, and Microsoft itself claims that Outlook blocks nearly 15 billion suspicious emails every day.
It’s important to understand the impact of phishing attacks, the different attack types and tactics, how to identify a phishing email, and the measures you should consider to protect your organization from these cyber threats. Written by a team of experts who provide data protection as a servicethis article covers all the basics so you can stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
The impact of phishing attacks
A large number of phishing attacks are motivated by financial gain, but this is not always the case. Gaining unauthorized access to an organization’s systems can serve a variety of malicious purposes, such as obtaining sensitive information for espionage or disrupting activities with malware for revenge or activism.
A phishing attack can cause a host of problems for organizations, including data breaches, reputational damage, operational disruptions and even regulatory fines.
Reducing risk starts with understanding the different types of phishing attacks your organization may face and the different tactics used.
Types and tactics
Main types of email phishing attacks you may encounter:
|
PHISHING TYPE |
DETAILS |
|
Spearfishing |
Attackers tailor emails to specific people. Unlike traditional phishing, which aims to deceive as many people as possible, spear phishing is targeted and personalized |
|
Whaling |
Attackers target senior managers who have significant power, access and influence within a company |
|
Clone phishing |
Attackers clone a legitimate email and replace an attachment/link with a malicious version |
|
Email bombing |
Attackers flood an email inbox with numerous spam emails to distract the victim from important emails |
|
Business Email Compromise (BEC) |
Attackers target companies that work with foreign suppliers and/or companies that regularly carry out wiring Handover payments |
|
Man in the Middle (MITM) |
Attackers secretly intercept and alter a line of communication between two people who think they are communicating with each other |
Common phishing tactics:
|
PHISHING TACTICS |
DETAILS |
|
Email spoofing |
Attackers create email messages with a spoofed sender address |
|
Manipulation of links |
Attackers use misspelled URLs or subdomains to trick people into thinking they are visiting a legitimate website |
|
Pop-up windows |
Attackers collect personal information or trick people into downloading malicious hardware through a pop-up window |
|
Image phishing |
Attackers embed malicious code into image files, which link to phishing websites |
|
Website spoofing |
Attackers create a fake domain that looks like a legitimate domain |
Top signs of a phishing email
Fortunately, there are a number of signs that can help you identify a phishing email.
The sender information, subject lines, content, and any attachments can all reveal a phishing attempt by a cybercriminal. So it’s important to check the name and address for inaccuracies or changes, make sure the email content matches the subject line, check for spelling mistakes, poor grammar, unusual language or urgent requests, and check for suspicious file extensions such as . exe, .scr, .zip, .docm, .js.
You also have to trust your instincts. If something seems amiss, proceed with caution and always report suspected phishing attempts to your organization’s IT or security team.
Protection against attacks
Phishing is a form of social engineering designed to exploit trust, curiosity and fear. An email that appears to come from a trusted colleague or reputable organization can sometimes trip up even the most cautious employee.
That’s why awareness training should be the first line of defense for any cybersecurity strategy. In addition, you must take into account strong technical defense mechanisms and a well-prepared cybersecurity policy. Overall, a multi-pronged approach is the best way to protect against phishing threats and reduce the risk of a data breach.
Consciousness training
Any training offered to staff should cover a wide range of topics, including password security, email filtering and reporting a suspected phishing email. Use real examples of targeted phishing attacks to ensure employees understand what to look for and how to spot the signs of foul play.
However, once the training session has been conducted, don’t consider the job “done.” Training should be provided regularly so that employees are aware of the latest updates on methods, practical tips and best practices.
Well-prepared cybersecurity policy
Your cybersecurity policy should outline the responsibilities of all employees and the steps they should take when they receive a suspected phishing email. The policy should also cover all aspects of cybersecurity, including password management, use of company devices, use of personal devices for company work and how to handle sensitive data.
Again, doing this once is not enough. Review and update the policy regularly to reflect any organizational or operational changes and ensure it is up to date with current threats and best practices.
Strong technical defense
It is important to ensure that your systems are regularly updated and protected against known threats, using specific anti-phishing and URL defense software.
The technical defenses that organizations should establish include:
DMARC – an anti-spoofing check that makes it difficult for phishers to send fake emails from your organization’s email address
SPF – Sender Policy Framework is an email authentication technique that prevents spammers from sending messages on behalf of your domain
DKIM – DomainKeys Identified Mail is an email authentication method designed to detect spoofed sender addresses (email spoofing)
Other technical considerations
You should also consider these important steps:
-
Restrict users’ rights to reduce the impact of potential breaches
-
Use multi-factor authentication
-
Consider implementing phishing filters for links and attachments, Protective Domain Name Service (PDNS), allowed application lists, remote browser isolation, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Keep in mind that a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy includes multiple preventative measures. You should not rely solely on technical security, or on the training and policies of your staff. The most effective strategy is one that includes all of these elements, as well as a well-planned response protocol to ensure quick action and minimal impact when incidents occur.
Do not panic
In the event of a phishing attack, it is important that you keep a cool head with your staff. If you have taken the right steps to protect yourself, there should be no need to panic. There are a number of useful, free cybersecurity resources worth exploring, outlined below.
The UK National Cyber Security Center offers a free check your cyber security service to help UK organizations check for cyber vulnerabilities.
The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) provides several tools and key services, including certification programs, events and guidance. Read more about ENISA’s services
Canada’s Communications Security Establishment (CSE) launched a national cybersecurity awareness campaign on October 1, 2022. Go cyber safe provides public information about cybersecurity and how to secure accounts, devices, and network connections.













