Health
Weight loss drug Zepbound can also treat obstructive sleep apnea. Here’s what you need to know about the disease
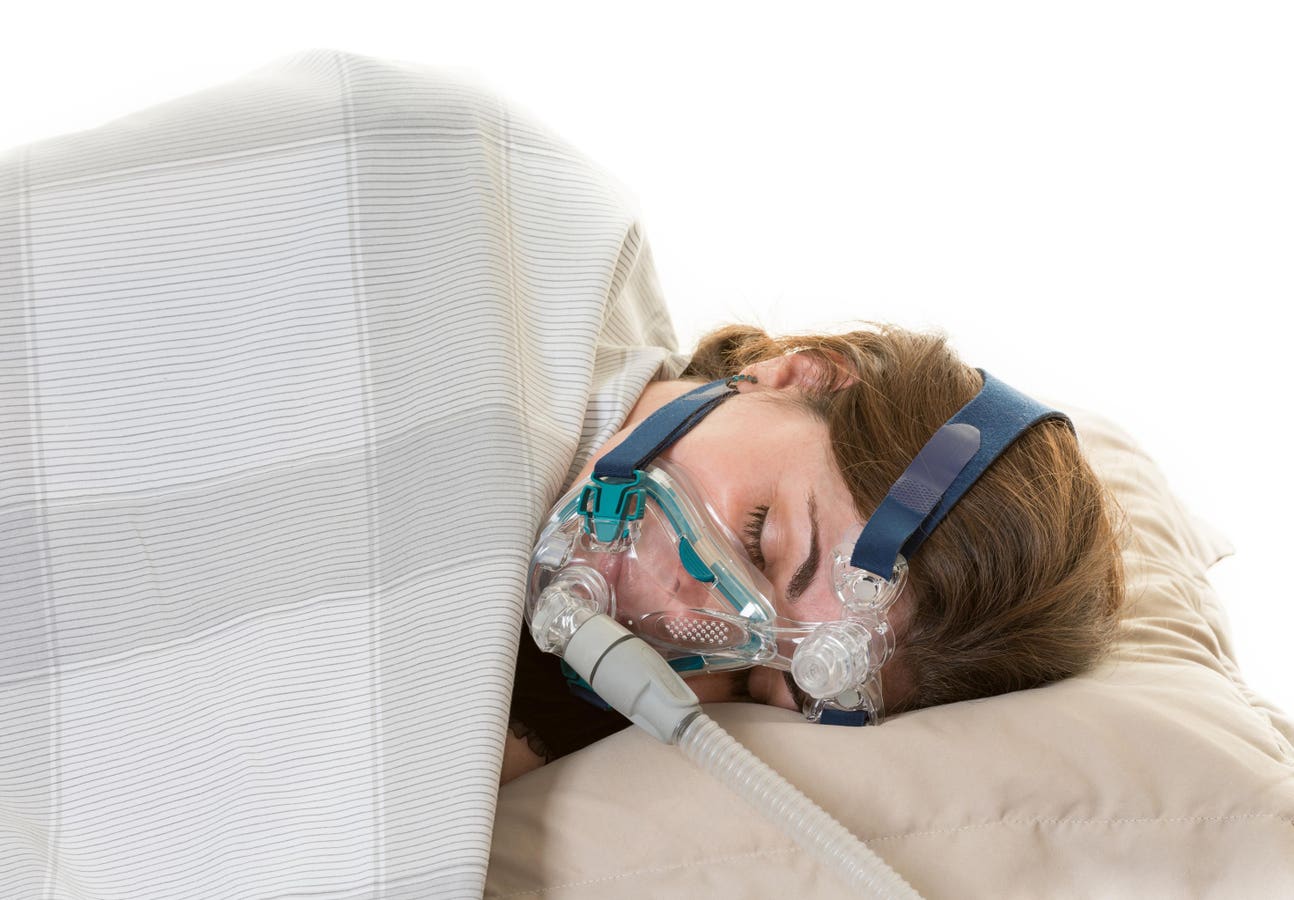
TORONTO, ONTARIO, CANADA – 04/12/2014: Woman wearing the CPAP mask for the treatment of sleep apnea … [+]
a clinical trial Efforts are underway to evaluate the efficacy of Zepbound, a popular weight-loss drug, to also treat obstructive sleep apnea. If Zepbound proves to be effective, it could potentially be covered by Medicare in the future, similar to how Wegovy will be covered, as the manufacturer showed a clinical benefit in treating diseases beyond just obesity; namely cardiovascular disease.
Nearly 30 million Americans suffer from obstructive sleep apnea, but only 6 million are diagnosed with it, according to the study. American Medical Association. The disease occurs when breathing is interrupted for more than ten seconds during sleep, at least five times per hour. This usually happens because the muscles around the throat relax during sleep, causing the airways to block and disrupt breathing. During normal daytime hours, the throat muscles keep the airways open to facilitate breathing. Given the millions of cases that go undiagnosed among Americans, raising awareness about the disease is critical.
Although anyone can eventually develop obstructive sleep apnea, it is more common in middle-aged and elderly people, as well as men. Additional risk factors for developing the disease include being overweight or obese, a large or thick neck, chronic nasal congestion, smoking, and anatomical abnormalities that result in airway blockage, such as enlarged tonsils or adenoids.
Some patients are diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea and have no symptoms. However, most people with the disease may snore and feel restless after sleeping because sleep quality is fragmented due to interruptions in breathing, and they may be irritable. Additional symptoms include morning headaches, depression, and falling asleep frequently during the day.
If you are diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea, you will usually need to visit your doctor and participate in a detailed history and physical examination, during which your doctor will likely ask you questions about your sleep and bedtime routine. In addition, your doctor will perform a detailed physical examination of your throat, neck, and mouth. The definitive way to diagnose the disease is through a sleep study, which can be performed at a specialized sleep center or even in the comfort of your home.
Various treatments for obstructive sleep apnea aim to improve sleep quality and resolve breathing disturbances. The primary treatment involves continuous positive airway pressure, or a machine connected to a mask that a patient puts on to deliver continuous air to keep the airway open during sleep. Additional treatments may include oral appliances and even surgery in more severe cases. Finally, behavioral changes such as losing weight and side sleeping can be very helpful in mitigating the severity of the disease.
The condition not only disrupts sleep, but can also have profound effects on overall health. Repeated interruptions in sleep can result in fatigue and excessive daytime sleepiness, which can result in irritability, as well as difficulty concentrating and impaired cognitive function. This can undoubtedly affect students’ productivity at work or concentration at school. Obstructive sleep apnea can also increase the risk cardiovascular disease. When breathing is interrupted for a period of time, oxygen levels in the blood drop, putting strain on the heart and raising blood pressure. The heart has to work harder to deliver enough oxygen to the blood, increasing the risk of high blood pressure, which invariably increases the risk of heart disease.
Importantly, many Americans with obstructive sleep apnea dismiss their symptoms as part of normal aging or may not be fully aware of the condition itself; According to research, 90% of people who have the disease do not even know they have the disease Johns Hopkins Medicine. Raising awareness of this critical public health condition should be of paramount importance to helping Americans understand, treat, and cope with the disease.